
The Internal and External Oblique Muscles Its Attachments and Actions
⭐ Internal Oblique Muscle Anatomy ⭐💪Origin: Thoracolumbar fascia, iliac crest and the inguinal ligament💪Insertion: Inferior margins of tenth to twelfth rib.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/7149/Abdominal_internal_oblique_muscle.png)
Internal oblique, external oblique, transversus muscle Kenhub
Internal abdominal oblique muscle is mainly supplied by the lower six thoracic spinal nerves (T7-T12), namely the terminal branches of the lower five intercostal nerves and the subcostal nerve. Additionally, the iliohypogastric and ilioinguinal nerves (L1) provide minor contributions to the nervous supply of this muscle.

External and Internal Oblique Muscles
The Obliquus internus abdominis ( Internal or ascending oblique muscle ), thinner and smaller than the Obliquus externus, beneath which it lies, is of an irregularly quadrilateral form, and situated at the lateral and anterior parts of the abdomen. It arises, by fleshy fibers, from the lateral half of the grooved upper surface of the inguinal.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13061/Internal_abdominal_oblique_muscle_copy.png)
Internal abdominal oblique Origin, insertion and action Kenhub
The internal oblique (L. internus, internal ; obliquus, oblique.) is a flat sheet of muscle on either the side of the lower torso. It gets its name from being beneath the external oblique and having an oblique fiber direction relative to the midline. The most prominent actions of the internal oblique are spinal lateral flexion and spinal rotation.

obliques Fit Forever
The internal obliques lie under the external obliques so they are the core's deeper muscles. O'Connor says you can visualize their location using this simple trick: "Imagine you had the.

Oblique Muscle The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary
The internal abdominal oblique muscle is one of the muscles of the abdomen. It is a broad, flat skeletal muscle. Adjacent to the midclavicular line, the muscle belly gives rise to a broad aponeurosis of internal abdominal oblique, which contributes to the formation of the anterior and posterior layers of the rectus sheath. The internal.

External and Internal Oblique Muscles
The internal obliques can function bilaterally, which means both sides work together. Bilaterally they flex the trunk and compress its contents. They can also function unilaterally, which means one-sided. Unilaterally, they laterally flex the trunk and rotate it to the same side. Like the internal obliques, the external obliques function.

The Internal and External Oblique Muscles Its Attachments and Actions
The internal oblique muscle is a muscle that is found at each side of the body, just lateral to the abdomen. The word 'oblique' means 'diagonal' or 'slanted', which is a reference to the slanted.
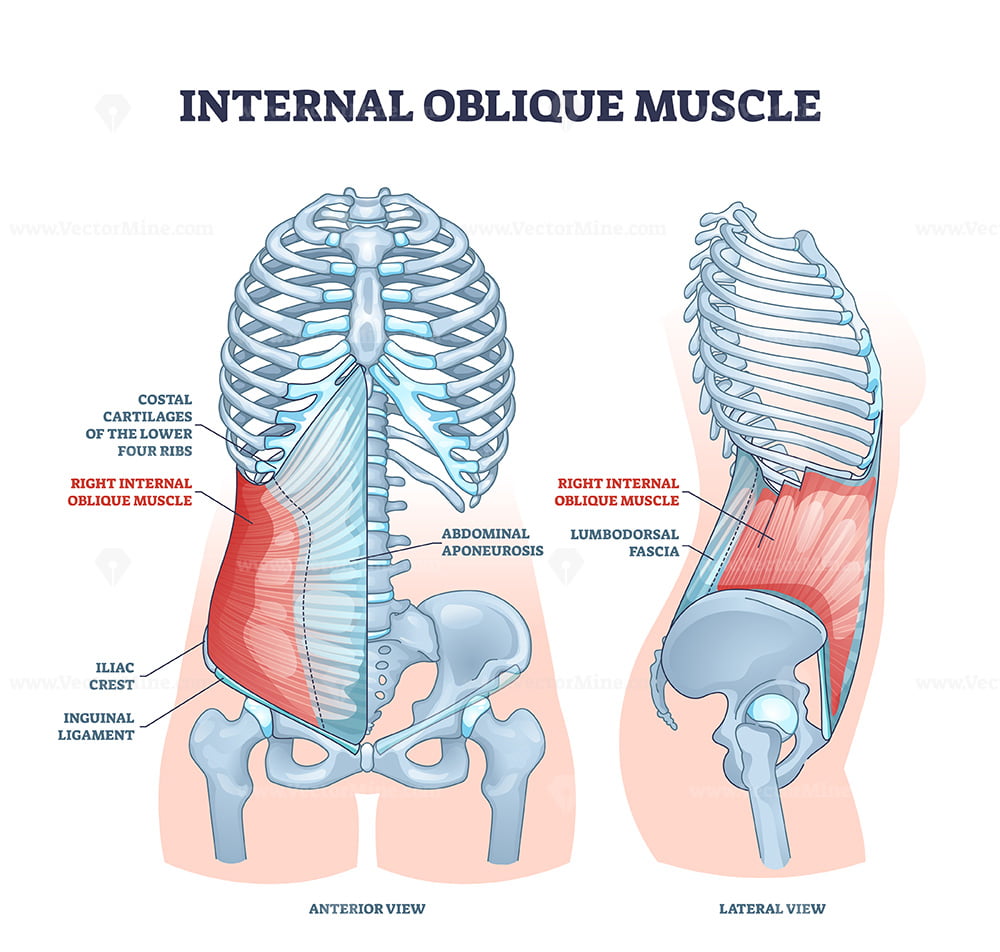
Internal oblique muscle with ribcage muscular system anatomy outline diagram VectorMine
Definition. Oblique muscle refers to two abdominal muscles - the external and internal obliques. These provide trunk flexion and rotation. The external oblique is the thickest and runs from the lower ribs to the iliac crest. The internal oblique lies under the external muscle and also originates at the iliac crest before reaching the pubic bone.

Spine Biomechanics Part 4 The Muscles of the Spine Biomechanics Education
The internal oblique muscle originates from the anterior two-thirds of the iliac crest and the thoracolumbar fascia. Its fibers diverge over the side of the trunk and insert along the structures of the midline, including the inferior margins of ribs 10-12, the linea alba, and the pubic crest. Origin and insertion of the internal abdominal oblique.

Internal and External Obliques Anatomy Origin, Insertion, Actions The Wellness Digest
Internal oblique, external oblique, and transversus abdominis muscles (from left to right) The external oblique muscle is a lateral flat muscle that courses from the 5th to the 12th rib ventromedially until the anterior layer of the rectus sheath. At its origin, it is tightly connected with the serratus anterior and latissimus dorsi muscles.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/en/the-lateral-abdominal-muscles/0rYd1fO40tMQrdUB4j6lrw_Musculus_obliquus_internus_abdominis_02.png)
Internal oblique, external oblique, transversus muscle Kenhub
abdominal internal oblique muscleinternal oblique muscle, is an that lies below the external oblique muscle and just above the transverse abdominal muscle. Its fibers run perpendicular to the , beginning in the thoracolumbar fascia of the lower back, the anterior 2/3 of the (upper part of hip bone) and the lateral half of the inguinal ligament.
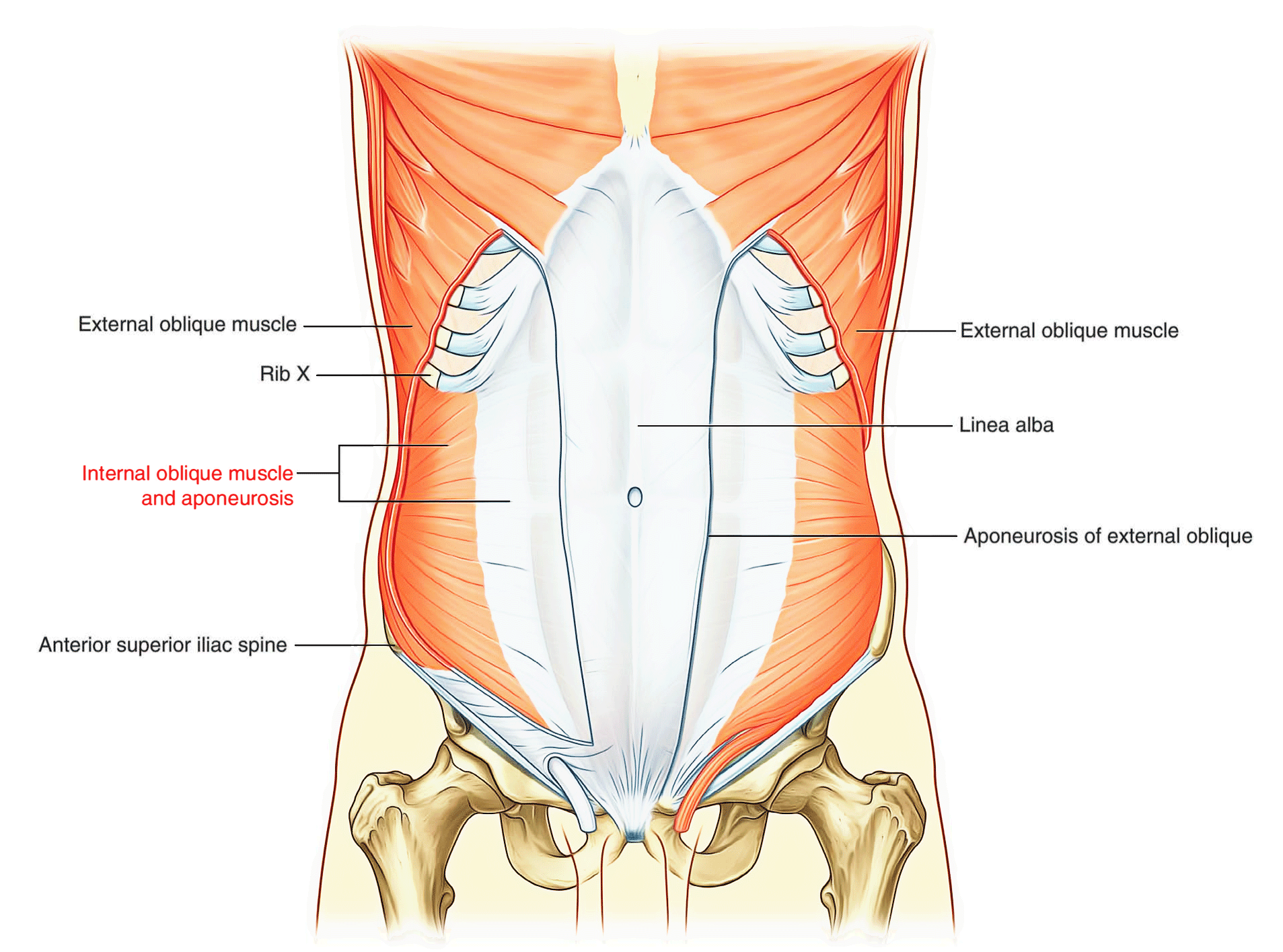
Easy Notes On 【Abdominal Wall】Learn in Just 3 Minutes! Earth's Lab
Internal obliques: The internal obliques are a pair of muscles on top of the external obliques, just inside your hip bones. Like the external obliques, they are on the sides of the rectus abdominis, running from the sides of your trunk toward the middle. They work with the external oblique muscles to allow the trunk to twist and turn.

Internal Obliques Learn Your Muscles Custom Pilates and Yoga
The internal oblique muscles are also innervated by the ilioinguinal nerve (L1). Transversus abdominis The final muscle in the abdominal area of the anterior trunk is the transversus abdominis muscle. It lies underneath the internal oblique muscle, hence it is the deepest flat muscle.

muscles of the chest at University of Wisconsin Green Bay StudyBlue
Transversus abdominis muscle: runs from the inner surface of the lower costal cartilages, the thoracolumbar fascia and iliac crest horizontally to the linea alba. Caudal fibers are involved in the formation of the cremaster muscle. The innervation is analogous to that of the internal oblique. The aponeuroses of the lateral abdominal muscles.
Obliques Exercises Obliques Workout ATHLEANX
The internal abdominal oblique muscle is an opposing force to the diaphragm, reducing upper chest cavity volume during exhalation. As the diaphragm contracts, the chest cavity is pulled down to.